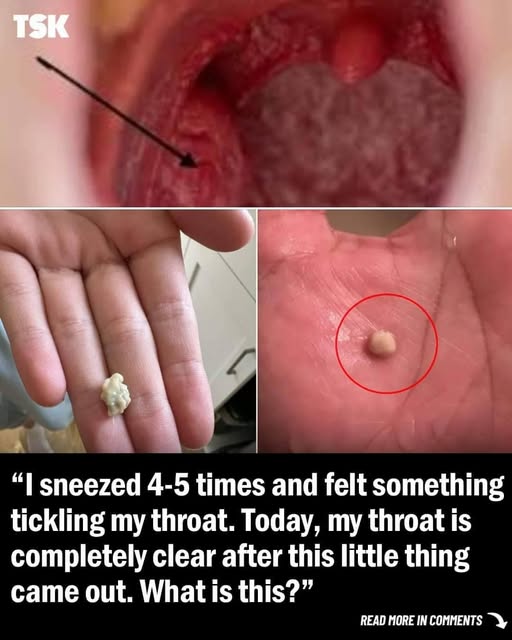
Tonsil stones, or tonsilloliths, are small, calcified deposits that form in the crevices of your tonsils. While often harmless, they can cause discomfort and bad breath. Let’s delve into what causes these pesky formations, how to recognize them, and the best ways to treat and prevent them.
What Are Tonsil Stones?
Your tonsils are glandular structures located at the back of your throat, playing a role in immune defense. They have tiny crevices known as crypts, where bacteria, dead cells, mucus, and food particles can become trapped. Over time, this debris can harden or calcify, forming tonsil stones.
Common Symptoms of Tonsil Stones
Many people with tonsil stones don’t experience noticeable symptoms. However, when symptoms do occur, they may include:
- Bad Breath (Halitosis): The accumulation of bacteria in tonsil stones can produce unpleasant odors, leading to persistent bad breath.
- Sore Throat: Tonsil stones can cause discomfort or pain in the throat, especially if they’re large.
- Difficulty Swallowing: Larger stones may make swallowing feel uncomfortable or challenging.
- Ear Pain: Though the stones are in the throat, they can cause a sensation of pain in the ear due to shared nerve pathways.
- Visible White or Yellow Debris: You might notice small white or yellow formations on your tonsils.
Causes of Tonsil Stones
Several factors can contribute to the formation of tonsil stones:
- Poor Oral Hygiene: Inadequate brushing and flossing can lead to bacterial buildup, increasing the risk of debris accumulation in the tonsils.
- Chronic Tonsillitis: Frequent inflammation of the tonsils can enlarge the crypts, making it easier for debris to become trapped.
- Sinus Issues: Post-nasal drip can lead to mucus collecting in the tonsils, contributing to stone formation.
Diagnosing Tonsil Stones
If you suspect you have tonsil stones, a healthcare provider can perform a physical examination of your mouth and throat. In some cases, imaging studies like CT scans or X-rays may be used to detect hidden stones.
Treatment Options for Tonsil Stones
Treatment depends on the size and symptoms of the tonsil stones:
- Gargling with Saltwater: This can help dislodge stones and soothe throat discomfort.
- Manual Removal: Using a cotton swab to gently remove the stone is possible, but caution is advised to avoid injury.
- Oral Irrigation: Devices like water flossers can help flush out debris from the tonsils.
- Laser Tonsil Cryptolysis: A procedure that reduces the number of crypts in the tonsils, decreasing the likelihood of stone formation.
- Tonsillectomy: In severe or recurrent cases, surgical removal of the tonsils may be considered.
Preventing Tonsil Stones
To reduce the risk of developing tonsil stones:
- Maintain Good Oral Hygiene: Brush and floss regularly to minimize bacterial buildup.
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking plenty of water helps keep the mouth clean and reduces debris accumulation.
- Treat Sinus Infections Promptly: Managing sinus issues can prevent mucus from collecting in the tonsils.
When to See a Doctor
If you experience persistent symptoms, such as chronic sore throat, difficulty swallowing, or notice large tonsil stones that don’t dislodge on their own, it’s advisable to consult a healthcare professional. They can provide appropriate treatment options tailored to your situation.
Conclusion
While tonsil stones can be a nuisance, understanding their causes and symptoms can help you manage and prevent them effectively. Maintaining good oral hygiene and seeking medical advice when necessary are key steps toward keeping your throat healthy and stone-free.